Earthquake Countermeasures for Buildings in Japan

In earthquake-prone Japan, we have been working on earthquake countermeasures for buildings for many years based on past earthquake experiences. Currently, huge earthquakes such as a Nankai Trough Earthquake and Tokyo Inland Earthquake are predicted throughout Japan. The Japanese Government is promoting earthquake-resistant housing and buildings as one of the ways to minimize their damages from such earthquakes that may come. Here, we would like to look at how much earthquake-resistant buildings in Japan have progressed, and how much quake-resistant buildings were effective in reducing damages in the past major earthquakes.
Earthquake resistance rate of Buildings in Japan
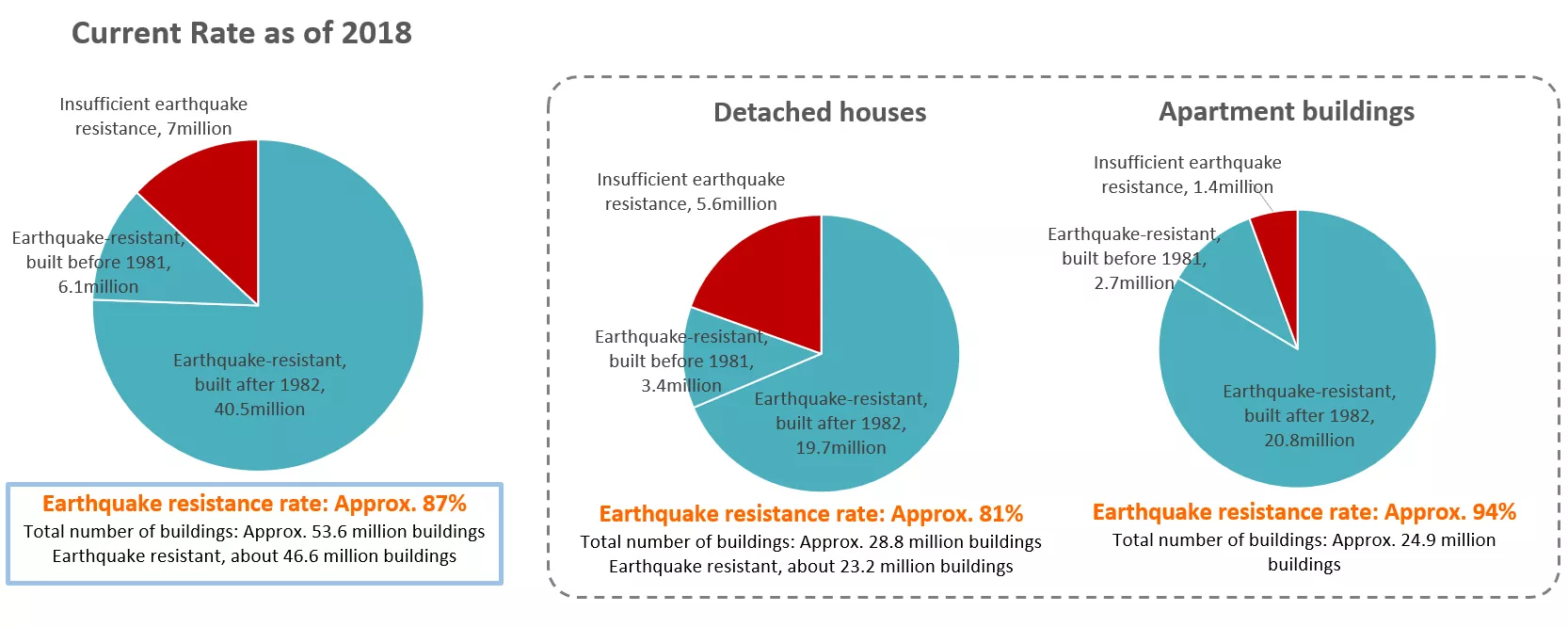
Looking at the data of the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism as of 2018, out of a total of about 53.6 million units, the earthquake resistant houses are about 46.6 million houses, and about 7 million houses come with insufficient earthquake resistance, and the earthquake resistance rate is about 87%.
The buildings constructed after 1982, under the “new earthquake resistance standards” based on Building Standards Act, are considered to be earthquake resistant. On the other hand, buildings built before 1981 are built according to the “old earthquake resistance standards” before the earthquake resistance standards were tightened, so the earthquake resistance is considered insufficient. But not all of them are dangerous, and out of the 13.1 million buildings that are built under the old earthquake resistance standards, about 6.1million buildings, whose quake-resistance performance were confirmed to be sufficient by seismic diagnosis or which completed seismic retrofitting works after the diagnosis, are earthquake-resistant.
Reference source from the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism materials
Looking at detached houses and apartment buildings, out of the total number of detached houses of about 28.8 million houses, about 23.2 million houses are earthquake-resistant and about 5.6 million houses are insufficiently earthquake-resistant, resulting in an earthquake resistance rate of about 81%. Out of the total number of apartment buildings of about 24.9 million, about 23.5 million are earthquake-resistant, and about 1.4 million are insufficiently earthquake-resistant, resulting in an earthquake resistance rate of about 94%.
The Japanese government supports seismic diagnosis and seismic retrofitting of the buildings constructed according to the "Old Earthquake Resistance Standards", with the goal of achieving an earthquake resistance rate of 95% by 2025 and mostly eliminating housing stock with insufficient earthquake resistance by 2030.
Acquisition Status of Seismic Grade for Buildings in Japan
As indicators of quake-resistance performance there are earthquake resistance standards and seismic grade. Here we would like to look at the acquisition status of Seismic Grade. It is one of the grades of the "Housing Performance Labeling System" based on the " Housing Quality Assurance Promotion Act (Housing Quality Assurance Act)" enforced in 2000. The higher the grade is, the higher the quake-resistance performance is.
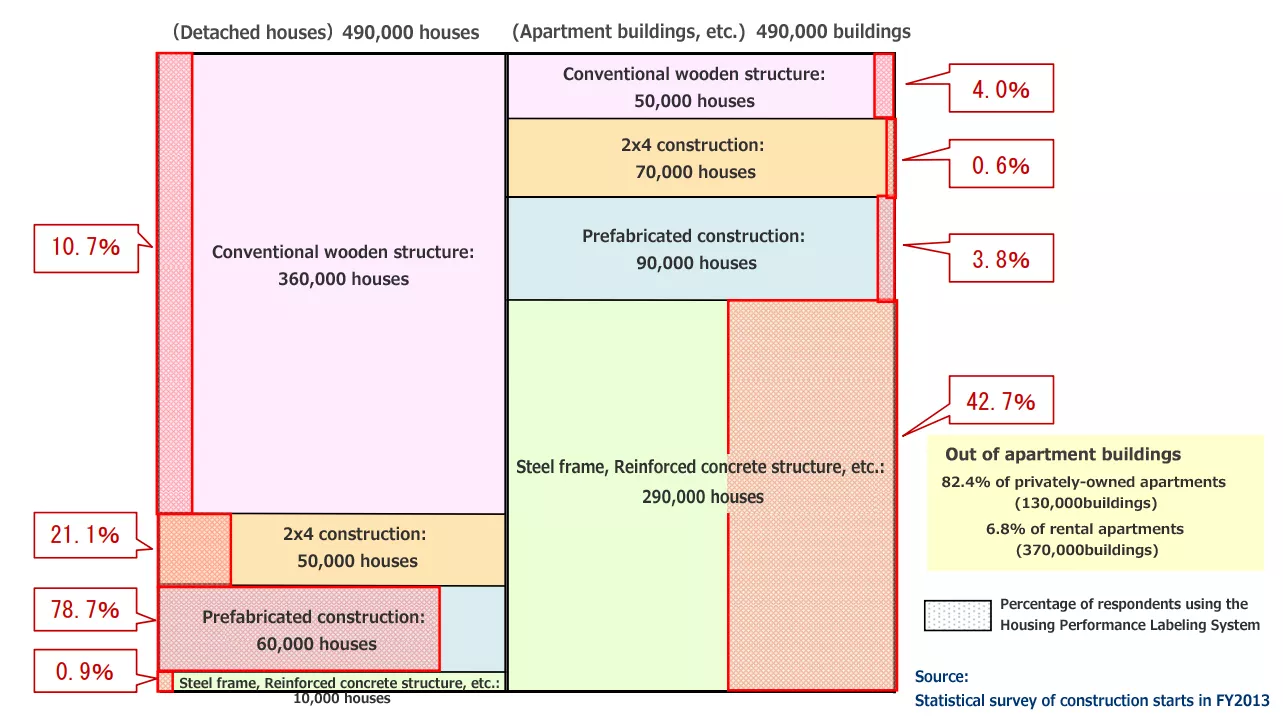
According to the study of usage of the Housing Performance Labeling System in fiscal 2013 disclosed by the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism, approximately 20% (approx. 100,000 detached houses, approx. 131,000 apartments) of the number of newly constructed buildings (approx. 990,000 buildings) used the Housing Performance Labeling System.
Usage Status of Housing Performance Labeling System for Newly Built Housing (in FY2013)
Reference source from the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism materials
About the ratio of the seismic grade obtained among detached houses, seismic grade 1 is about 10%, the grade 2 is about 6.6%, and the grade 3 is about 83%. About newly built houses that use Housing Performance Labeling System, more than 80% of them have obtained the grade 3 that is the highest seismic grade currently.
About apartment buildings, 42.7% of them with steel frames and reinforced concrete structures use Housing Performance Labeling System. Looking at the ratio of the seismic grade obtained, the grade 1 is about 87%, the grade 2 is about 8.5%, and the grade 3 is about 1.2%. This result shows that about 90% of apartment buildings are the seismic grade 1. The reason why the number of obtaining the seismic grade 2 or higher is less in apartment buildings than in detached houses is that; in order to improve the quake-resistance performance of large buildings such as apartment buildings, it is necessary to increase wall thickness and reduce windows, so flexibility of room planning is limited, and it is difficult to secure comfortable living spaces.
Earthquake Countermeasures of Apartment Buildings
About the earthquake countermeasures of apartment buildings, some apartment buildings adopt seismic isolation structures and damping structures to ensure quake-resistance performance in addition to commonly adopted earthquake resistant structures. Supply of the apartments with seismic isolation structure and damping structures has been increasing since the mid-1990s, and they have been widely introduced especially in high-rise apartment buildings with more than 30 floors.
We have looked at the status of earthquake resistance and the earthquake countermeasures of buildings in Japan so far. Japan has been repeatedly hit by earthquakes and has reviewed the earthquake resistance standards. Here we would like to look at the data of damage situation to see how much damage was suffered from the past huge earthquakes.
Damage from the Great Hanshin-Awaji Earthquake of 1995 (maximum seismic intensity scale 7)
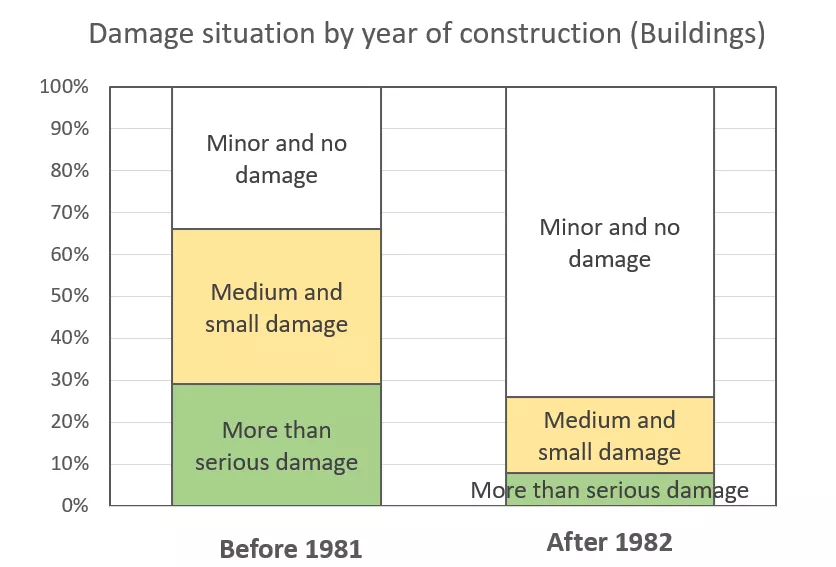
In the Great Hanshin-Awaji Earthquake, there was a difference in the damage situation between buildings with the old earthquake resistance standards and buildings with the new earthquake resistance standards. Only about 10% of the buildings with the new earthquake resistance standards had some damages while about 30% of those with the old earthquake resistance standards had more than serious damages (wreck, collapse). About 75% of the buildings with the new earthquake resistance standards could reduce the damages to minor or no damage. This damage situation found that the buildings with the new earthquake resistance standards could withstand earthquakes with JMA seismic intensity scale 6+ to 7.
Reference source from the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism materials
Damage from the 2016 Kumamoto Earthquake (maximum seismic intensity scale 7)
The damages of wooden buildings from the Kumamoto Earthquake in particular varied greatly depending on the year of construction. The collapse rate of the buildings with the old earthquake resistance standards (before May 1981) was 28.2%, which was significantly higher than the collapse rate of 8.7% for the buildings with the new earthquake resistance standards (after June 1981). Furthermore, the collapse rate of the buildings constructed after the revision of the Building Standard Act in 2000 was only 2.2%. 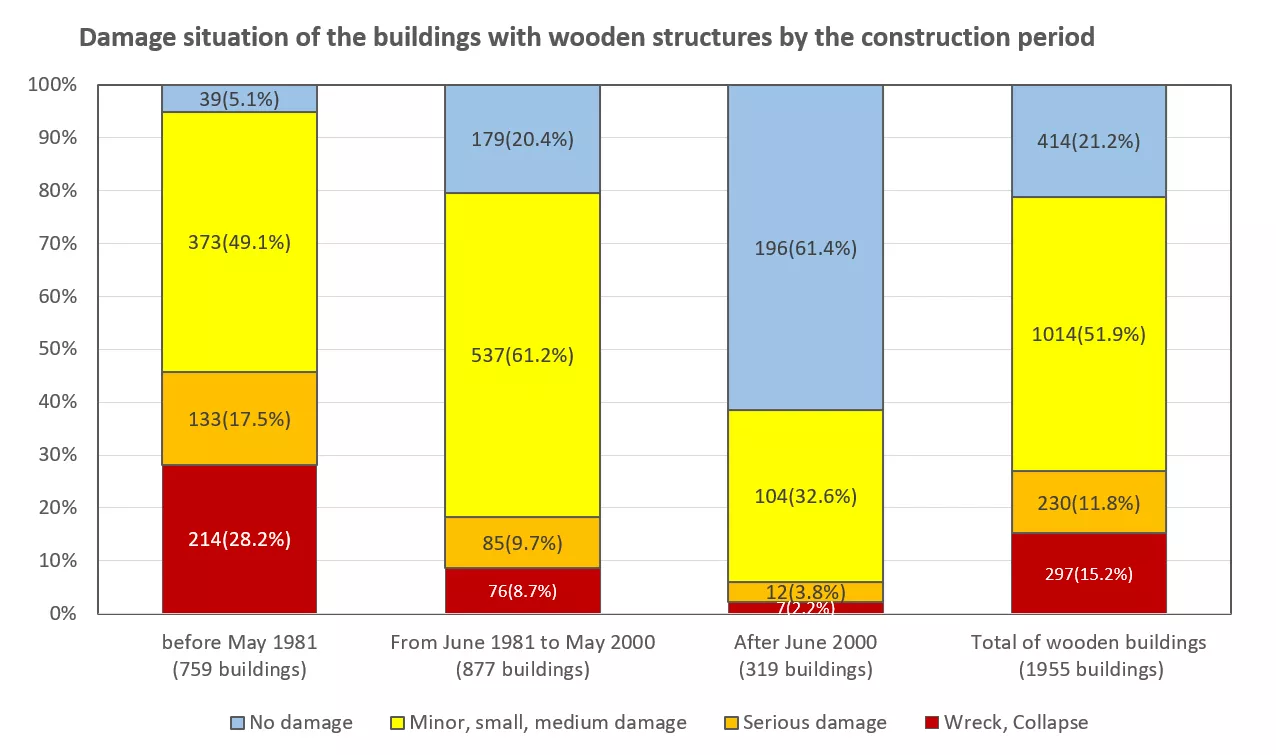
Reference source from the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism materials
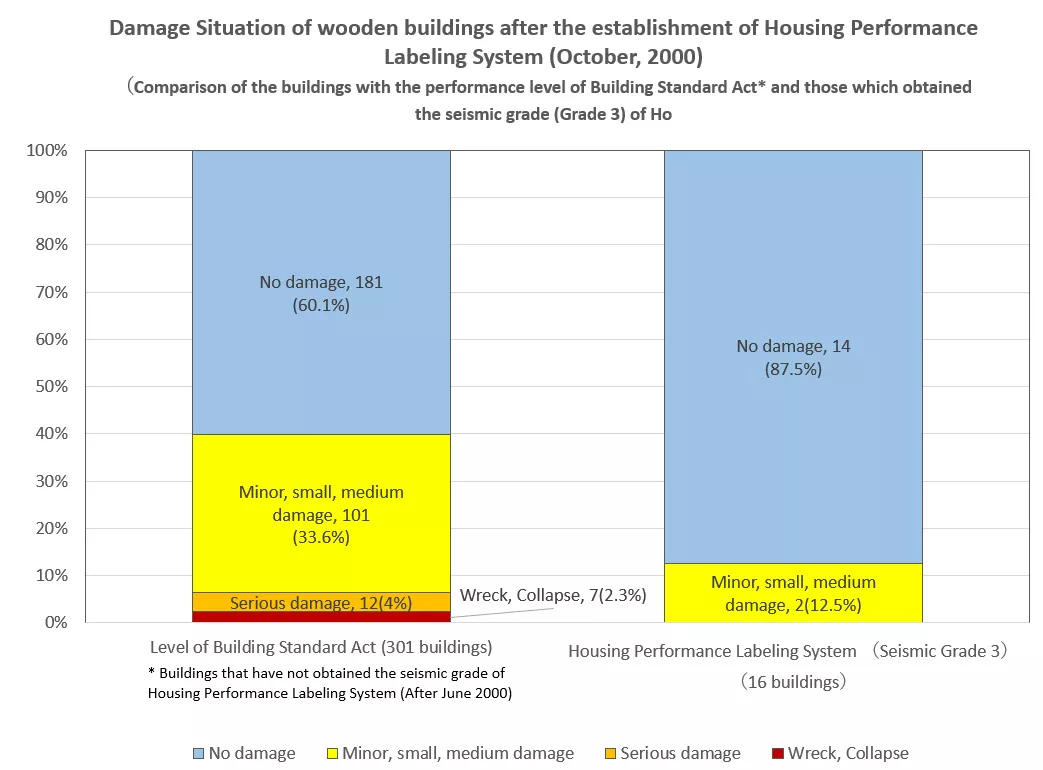
Buildings with Seismic Grade 3 of Housing Performance Labeling System were not so much damaged, and 87.5% of them were not damaged.
<Reference> Seismic grade of Housing Performance Labeling System (prevention of collapse, etc.)
This system is to verify and label the quake-resistance level to the extent that the buildings do not collapse against the force of "extremely rare huge earthquakes" that occur about once every few hundred years which are assumed in the Building Standard Act, as much as the following rate of the force of earthquakes:
・Grade 1 is 1 times (Level of Building Standard Act)
・Grade 2 is 1.25 times
・Grade 3 is 1.5 times
Reference source from the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism materials
No collapse of steel-framed or reinforced concrete buildings that met the new earthquake resistance standards was confirmed, and here again, it was shown that the new earthquake resistance standards are effective in preventing collapse against earthquakes.

- Rental Apartments & Houses in Tokyo
- Listings of popular and luxurious rental apartments, condominiums, and houses designed with expats in mind.

- Apartments & Houses for Sale in Tokyo
- Listings of apartments, condominiums, and houses available for purchase in Tokyo.



























