Land Use Zones under the City Planning Law in Japan

Land Use Zones (用途地域) are areas that are regulated under the City Planning Law (都市計画法) and designates the possible usage of land and properties in that area.
This system is to realize an effective placement of buildings in accord with each area environment, avoiding mixed and disorderly land usage such as for factories, commercial facilities, and housing.
If you are planning to purchase real estate properties or to build new homes in Japan, it is recommended that you understand Land Use Zones and the details of all the categories, because the neighborhood environment and what you can build may be different in each Land Use Zone.
Land Use Zones can be generally categorized into residential, commercial and industrial uses, and there are 13 zone categories in total.
In 2018, “Countryside Residential Zone” was newly added to Land Use Zones. This new Land Use Zone was created in order to protect agricultural land in urban areas, being concerned that many Productive Green Areas will be put up for sale all at once upon the expiration of The Productive Green Land Act in 2022, which was enacted in 1992 to designate agricultural land as Productive Green Land that can receive tax incentives, etc. When the tax incentives are terminated, a lot of such agricultural lands may be put up for sale, and such lands sold may be neglected without being used for residential lands. Countryside Residential Zone was created to prevent such neglected lands and “to protect a good housing environment related to low-rise housing while improving the convenience of agriculture”.
In “Countryside Residential Zone”, it is allowed to build stores and restaurants necessary to improve the convenience of agriculture, facilities used for collecting and storing agricultural products, storage facilities for agricultural machinery, etc., in addition to those that are allowed to build in Exclusively low-rise residential zone.
Land Use Zone
Residential Use
| Zoning | Image |
|---|---|
Category Ⅰ exclusively low-rise residential zoneThis zone is designated for low rise residential buildings. The permitted buildings include residential buildings which are also used as small shops or offices and elementary/junior high school buildings. The permitted buildings include residential buildings which are also used as small shops or offices and elementary/junior high school buildings. |
 |
Category Ⅱ Exclusively low-rise residential zoneThis zone is mainly designated for low rise residential buildings. In addition to elementary/junior high school buildings, certain types of shop buildings with a floor area of up to 150m2 are permitted. |
 |
Category Ⅰ mid/high-rise oriented residential zoneThis zone is designated for medium to high residential buildings. In addition to hospital and university buildings, certain types of shop buildings with a floor area of up to 500m2 are permitted. |
 |
Category Ⅱ mid/high-rise oriented residential zoneThis zone is mainly designated for medium to high rise residential buildings. In addition to hospital and university buildings, the permitted buildings include certain shops and office buildings with a floor area of up to 1,500m2 to provide conveniences for the local community. |
 |
Category Ⅰ residential zoneThis zone is designated to protect the residential environment. The permitted buildings include shops, offices and hotel buildings with a floor area of up to 3,000m2. |
 |
Category Ⅱ residential zoneThis zone is designated to mainly protect the residential environment. The permitted buildings include shops, offices and hotel buildings as well as buildings with karaoke box. |
 |
Quasi-residential zoneThis zone is designated to allow the introduction of vehicle-related facilities along roads while protecting the residential environment in harmony with such facilities. |
 |
Countryside Residential ZoneThis zone is designated to promote the use of agriculture and to protect a good housing environment related to low-rise housing in harmony with the agricultural use. |
 |
Commercial Use
| Zoning | Image |
|---|---|
Neighborhood commercial zoneThis zone is designated to provide daily shopping facilities for the neighborhood residents. In addition to residential and shop buildings, small factory buildings are permitted. |
 |
Commercial zoneBanks, cinemas, restaurants and department stores are constructed in this zone. Residential buildings and small factory buildings are also permitted. |
 |
Industrial Use
| Zoning | Image |
|---|---|
Quasi-industrial zoneThis zone is mainly occupied by light industrial facilities and service facilities. Almost all types of factories are permitted excepting those which are considered to considerably worsen the environment. |
 |
Industrial zoneAny type of factory can be built in this zone. While residential and shop buildings can be constructed, school, hospital and hotel buildings are not permitted. |
 |
Exclusively industrial zoneThis zone is designated for factories. While all types of factory buildings are permitted, residential, shop, school, hospital and hotel buildings cannot be constructed. |
 |
Each Land Use Zone puts restrictions on the volume, the height of buildings, as well as the way they can be used under provisions of the Building Standard Law.
When you build your home (or any new construction, enlargement or reconstruction), you must comply with the regulation in each Land Use Zone for the designated usage, and also must be within the limits of building volume and height.
The same regulations are applied when you change the usage of the existing building, and hence it must always comply with the specified type of land use.
Example) Category I Exclusively low-rise residential zone
You can build general housing, a small house and office, a small house and store, an elementary/junior high/high school, a nursing home, a library, a medical office, or a nursery school.
This zone is characterized as a low-rise building area where the majority of properties are single standing houses and low-rise apartments. The restrictions of maximum floor-area ratio and building height limits are the most severe. A safe and quiet residential environment can be secured in this zone because large-scale stores or amusement facilities where a lot of people gather cannot be built.
Control of Building Use by Land Use Zones
See the chart below:
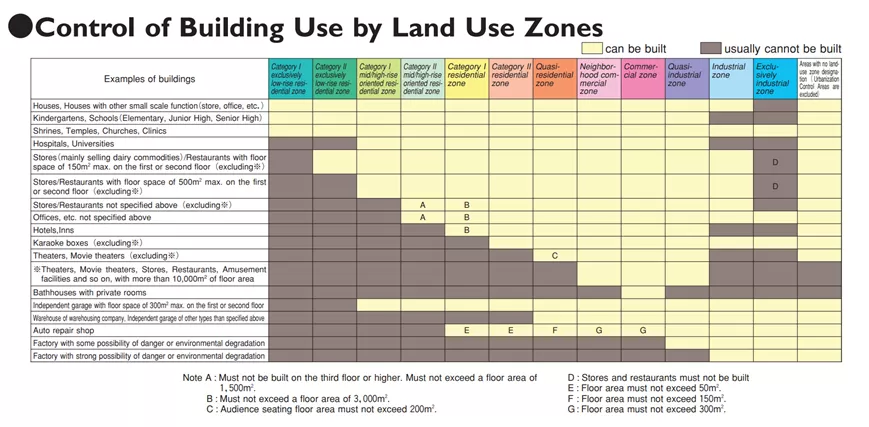
According to the website of Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism
English version: http://www.mlit.go.jp/common/001050453.pdf
When the local governments such as ward offices are showing Land Use Zones on their website, you can also visit and confirm there (the website is in Japanese).
Example)
Shibuya-Ku, City planning map : https://www.city.shibuya.tokyo.jp/
BUREAU OF URBAN DEVELOPMENT TOKYO METROPOLITAN GOVERNMENT : https://www2.wagmap.jp/tokyo_tokeizu/

- Apartments and Houses for Sale in Tokyo
- Listings of apartments, condominiums, and houses available for purchase in Tokyo.

- Sell your Tokyo Property
- PLAZA HOMES’s bilingual real estate experts offer a wealth of local knowledge on how to effectively sell your property in Japan.























