Compliance with energy conservation standards will become mandatory from April 2025. What is the impact on the asset value of real estate?
In April 2025, compliance with energy conservation standards for newly built houses will become mandatory in Japan. Those who are purchasing or building a house in the future will need to understand the energy conservation standards. The goal is to achieve even higher energy-saving performance (ZEH standard) by 2030, and energy conservation standards for newly built housing will be raised in stages in the future. By clearly indicating the energy-saving performance of a house, buyers will be able to choose a house that is healthier and more comfortable to live in.
In addition, houses that meet energy conservation standards are eligible for subsidies and housing loan tax deductions, so it is expected that energy conservation standards for houses will become one of the important factors for housing buyers to make decisions in the future.
This article explains the background on the mandatory energy conservation standards, an overview of energy-efficient housing, and the impact on the housing market in the future.
What are energy-saving performance and energy conservation standards?
1. Background of Mandatory Compliance with Energy Conservation Standards
In response to the global issue of climate change, efforts are underway around the world to achieve carbon neutrality, or to reduce greenhouse gas emissions to “virtually” zero. Japan has declared its goal of achieving carbon neutrality by 2050, with a 46% reduction in greenhouse gas emissions by 2030 compared to 2013 levels. In response to this, in order to accelerate energy conservation measures in the building sector, which accounts for approximately 30% of Japan's energy consumption, compliance with energy conservation standards, that improve the thermal insulation performance of buildings and promote the use of renewable energy, will be mandatory for a wide range of buildings starting in April 2025.
2. What are energy-saving performance and energy conservation standards?
A house with high energy-saving performance is one that combines heat insulation performance that keeps cold air in winter and hot air in summer out of the rooms and keeps the building warm or cool using less energy, with energy-efficient air conditioners, lighting, water heaters, and other equipment.
The energy conservation standards stipulate the standards for building structure and equipment necessary to ensure the energy-saving performance that buildings should have, and consist of 2 standards, “Building Palstar Index (BPI) (Thermal Insulation Performance (TIP))” and “Building Energy Index (BEI),” each of which must be satisfied.
| Building Palstar Index (BPI) (Thermal Insulation Performance (TIP)) The outer shell refers to the part of a building that separates the interior from the outside, including exterior walls, windows, floors, roofs, and ceilings. A high thermal insulation performance of the exterior skin and solar radiation shielding performance (performance to prevent solar radiation) makes the building less affected by the outside temperature, thereby enhances the energy-saving performance of the building. There are seven grades from 1 to 7, with higher numbers indicating better thermal insulation performance. |

| Primary Energy Consumption It represents the amount of energy consumed per year by air conditioning, ventilation, lighting, hot water supply, etc., which is obtained by deducting the energy generated by solar power generation facilities, etc. Existing houses are expressed as approx. grade 3, being expressed by grades 3-6, and the higher the number, the more energy-saving the house. |

3. What energy conservation standards will be mandatory to comply with from April 2025?

“Thermal Insulation Performance (TIP) Grade” and “Building Energy Index (BEI) Grade”
From April 2025, all houses will be required to meet Thermal Insulation Performance Grade 4 and Primary Energy Consumption Grade 4 or higher. Since it will be mandatory to obtain a determination of conformity with energy conservation standards when applying for building permits, construction work cannot be started until compliance with the standards has been confirmed.
4. Mandatory compliance is scheduled to be raised to ZEH standard level in 2030
Energy conservation standards were first established in 1980 in response to the Energy Conservation Act (Act on the Rational Use of Energy) and have been revised many times since then. Standards have been raised for the first time in about 20 years since 1992, with new Thermal Insulation Performance grades 5, 6, and 7 in 2022 and new Building Energy Index grade 6 in 2023. Before that, Thermal Insulation Performance grade 4 was the highest grade, but after April 2025 it will be the lowest grade. In addition, in 2030 energy conservation standards will be raised to the ZEH standard level, which will require Thermal Insulation Performance Grade 5 and Building Energy Index Grade 6.
Advantages and disadvantages of energy conservation standard compliant housing
Energy-efficient houses that are environmentally friendly and comfortable to live in have many advantages, but there are also some precautions. Let's take a look at the advantages and disadvantages.
Advantages of energy conservation standard compliant housing
● You can live comfortably throughout the year
With its high thermal insulation performance, it is less susceptible to the influence of outside temperatures, allowing you to stay warm in winter and cool in summer. The temperature difference in the room can be reduced, and the room is kept at a comfortable temperature, reducing the risk of heat shock caused by sudden temperature differences and heat stroke in summer.
● Being energy efficient, it saves money
The use of air conditioning and hot water heaters with high thermal insulation performance and energy efficiency reduces the use of air conditioning and heating, which reduces utility costs and saves household budgets.
● You can receive tax benefits and tax deductions.
With its energy-saving performance, you can receive housing loan tax deduction and tax benefits of real estate acquisition tax. If you build a new house after the year 2024, newly built houses that do not meet energy conservation standards will not be eligible for the housing loan tax deduction. For details, please refer to Tax deduction Program for Energy-efficient Housing.
Disadvantages of energy conservation standard compliant housing
● The cost of construction and equipment will be high
Houses that meet energy conservation standards use heat insulating materials, windows, and equipment with high energy-saving performance, so construction costs are high. Since houses that do not meet energy conservation standards cannot be built, the option of low-cost housing with low energy-saving performance is eliminated, and the sales price of newly-built houses is expected to be higher.
● Possible cost reductions that do not affect energy conservation standards to be noted
To keep the sales price down, cost reductions may be made by using lower grade equipment or not installing some equipment.
Tax deduction Program for Energy-efficient Housing
It is important to note that the energy conservation standards of housing are a condition for receiving tax benefits when purchasing a house.
1. Housing Loan Tax Deduction
Housing loan tax deduction is a tax deduction program available to those who purchase a house using a housing loan. 0.7% of the outstanding loan balance at the end of the year is deducted from income tax and inhabitant tax over a period of up to 13 years.
Overview of Housing Loan Tax Deduction (after tax reform in FY Reiwa 6 (FY2024))
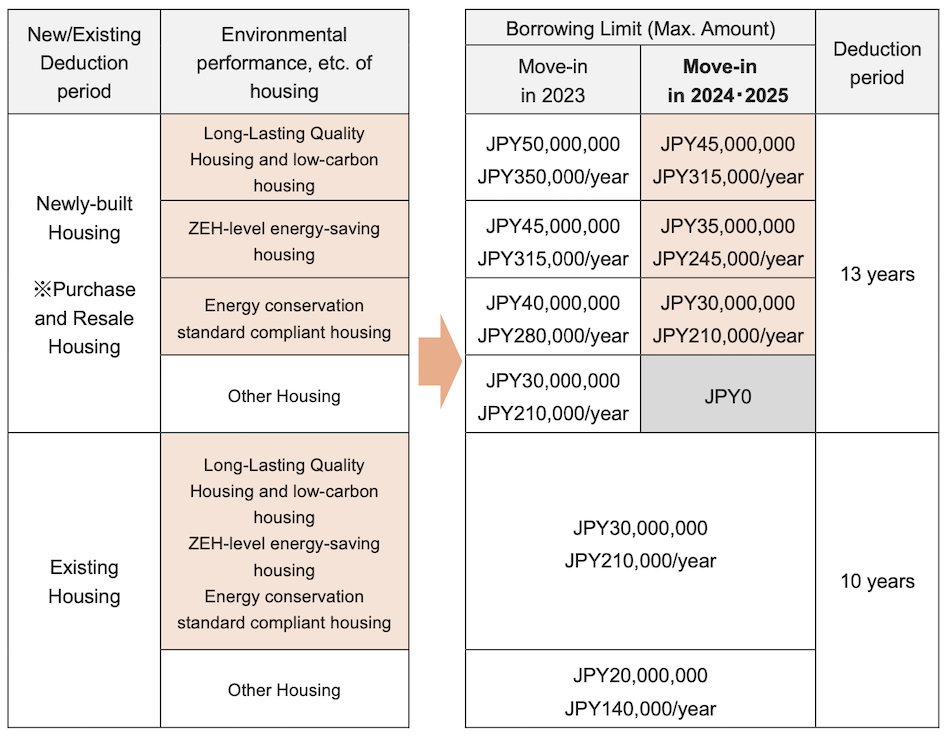
For newly built houses that receive building permits after January 2024, compliance with energy conservation standards will be mandatory, and houses that do not meet the standards will not be eligible for housing loan deductions. In addition, houses with higher energy-saving performance receive more generous tax benefits.
2. Other Tax Incentives
In addition to housing loan tax deductions, there are other tax incentives for energy-efficient homes.
・Real estate acquisition tax
This is a tax imposed on the acquisition of real estate such as a house or land. In the case of a newly built house with long-lasting quality, the deduction amount is larger than that of ordinary housing.
・Registration and license tax
When a home is purchased, the purchaser's ownership is registered for preservation, and this tax is paid when applying for registration. In the case of long-lasting quality housing and newly built low-carbon housing, the tax rate related to the registration of preservation of ownership will be reduced more than that of the special provisions for general housing.
・Property tax
In the case of the acquisition of a newly built long-lasting quality housing, the applicable period of the tax deduction will be extended from 3 years for ordinary housing to 5 years.
Compliance with energy conservation standards will be mandatory from April 2025, and the standards are scheduled to be raised in the future. Since the government is promoting the increase of energy-efficient housing through tax deductions for housing loans, etc. and subsidies, energy-saving performance will become an indicator that home buyers will have no choice but to pay attention to. If you are considering the purchase of a house in the future, we recommend that you choose a house with higher energy-saving performance in anticipation of an era in which energy-saving performance determines your property values.

- Apartments & Houses for Sale in Tokyo
- Listings of apartments, condominiums, and houses available for purchase in Tokyo.




















